Battery electric vehicles (BEV) are the clear winner when trying to reduce emissions in the transportation sector, according to Rystad Energy research. Despite incurring higher emissions in the manufacturing process of electric vehicles and an enduring reliance on fossil fuel power generation in many countries, the positive environmental impact of switching to a BEV over the vehicle’s lifetime is unmistakable.
Our analysis shows that battery-powered vehicles contribute at most half the carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) of diesel or gasoline cars across their lifecycle, regardless of the country of operation. Even in countries where the power grid is dominated by fossil fuels, battery-powered cars emit about 50% of the CO2e of an internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle. As renewable sources replace coal and gas-fired generation, emissions related to the operation of BEVs could drop by 86%.
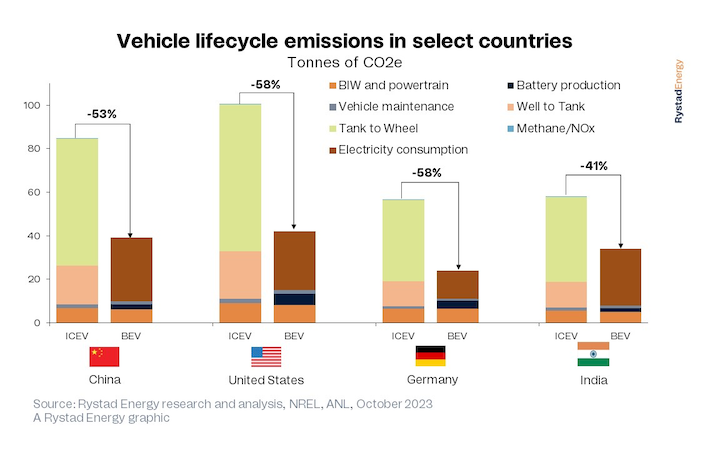
Our in-depth research of lifecycle BEV and ICE vehicle emissions considers every stage of the manufacturing process and the vehicle’s operation. This includes the manufacturing of the vehicle’s body, known as body in white (BIW), powertrain assembly, maintenance, fuel and electricity-related emissions and battery production for BEVs. We are conscious that there are often societal and humanitarian impacts associated with EV manufacturing, battery production and associated mining. However, this research is purely focused on the emissions comparison between battery electric and traditional-fuel vehicles.
Based on the current power generation mix in China, the lifecycle emissions of a BEV are about 39 tonnes of CO2e versus almost 85 tonnes for an ICE vehicle. The difference in the US is even starker. A BEV emits 42 tonnes of CO2e across its life in the US, 58% lower than a gasoline or diesel vehicle that emits more than 100 tonnes. Of these totals, emissions related to the extraction, refining and burning of fossil fuels contribute about 90% of all ICE emissions. The breakdown of emissions across a battery-powered vehicle’s life is directly tied to its electricity consumption and how that power is generated.
“Overall, battery electric vehicles are clearly the right technology to reduce emissions in the transportation sector. Switching to a BEV will reduce long-term emissions despite a larger environmental impact at the beginning of the vehicle's life. Contrary to some claims, electric car adoption is not a fool’s errand; it will slash emissions in the long run and accelerate the energy transition,” said Abhishek Murali, senior clean tech analyst with Rystad Energy.